Structural Due Diligence (With Forensic Science)
forensic structural engineering
structural forensics
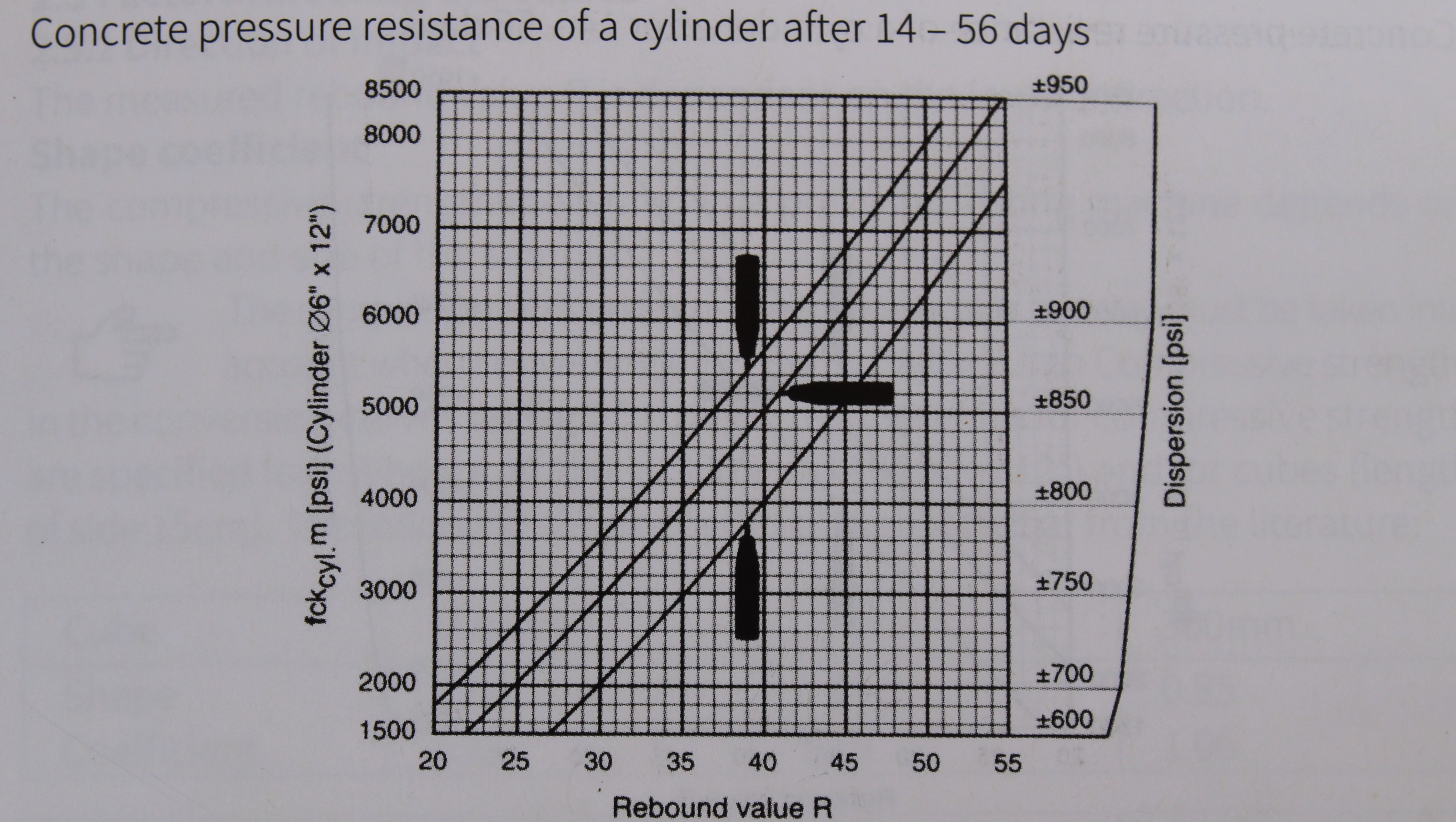
non- destructive testing in concrete
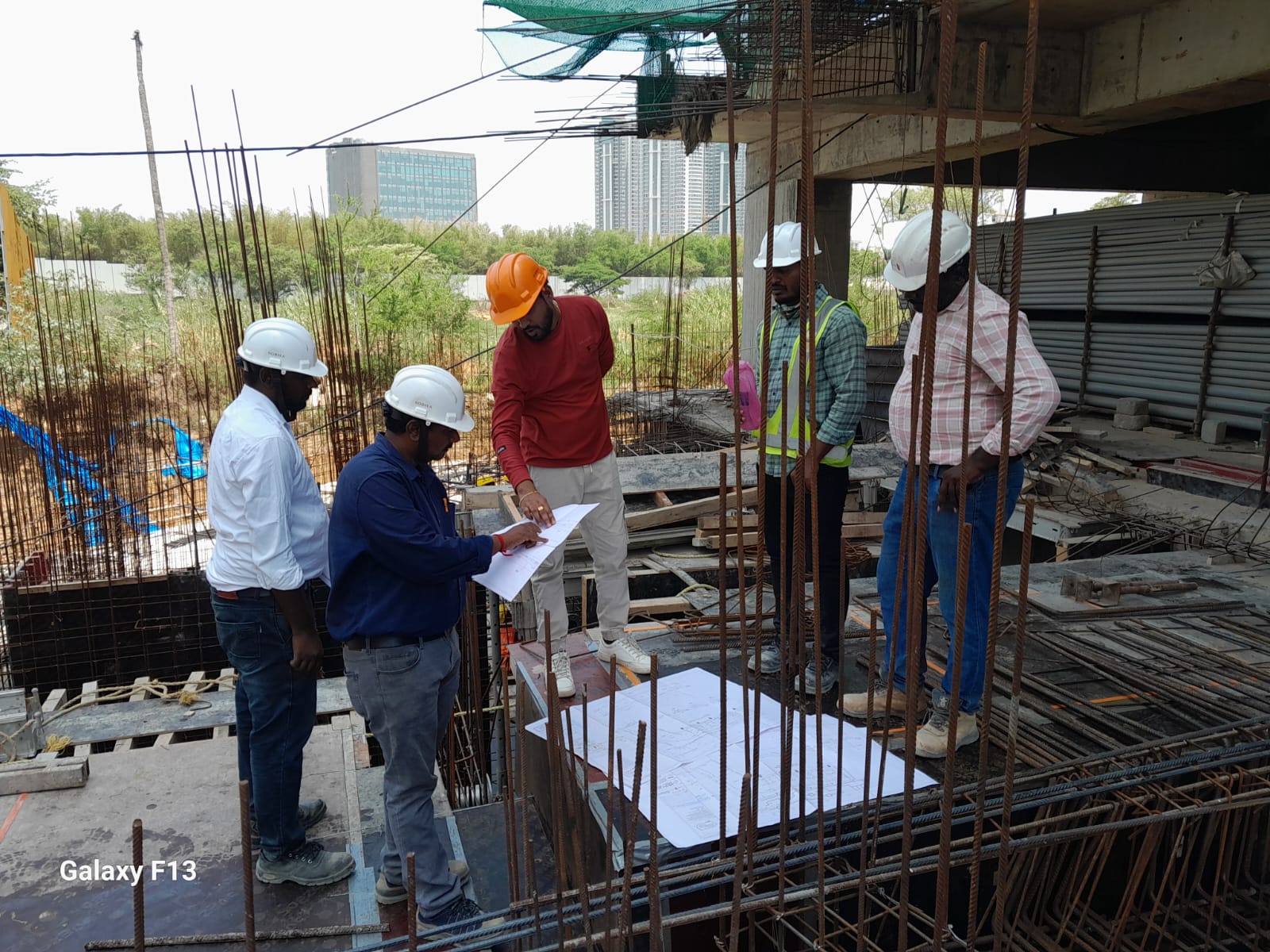
Our specialized Structural Due Diligence services involve comprehensive assessments of existing structures through detailed desktop study, site visits and Non-Destructive Testing (NDT). We meticulously evaluate their condition, safety and compliance with codes and standards employing techniques from structural forensics to uncover hidden issues. Our rigorous process yields crucial insights for informed decision-making in property acquisitions or investments, ensuring a solid foundation for projects. With a track record encompassing successful project completions totalling over 50+ million square feet, our assessments provide peace of mind and confidence in property transactions and investments.
Structural Due Diligence helps clients make informed decisions about their buildings that in turn helps them in buying or selling of properties and for the change of use of a particular building.